
Antibodies for Cancer Immunology
Cancer immunotherapies exploit subtly different molecules, such as proteins and carbohydrates, on the cell surface of tumor cells, which can be detected by the immune system. Immunotherapy activates the immune system by detecting these molecular antigens and targeting the tumor cells. Immune checkpoint ligands, such as PD-L1, are often times upregulated in tumor cells and using immune checkpoint proteins has become a method to target cancer treatment. Further, targeting immune-checkpoint proteins is another important area of focus as these proteins are often times dysregulated by tumors.
|
|
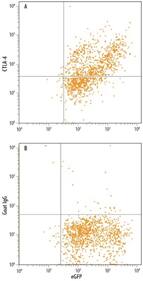 |
| Flow Cytometry: CTLA-4 Antibody [AF-386-PB] - NS0 mouse myeloma cell line co-transfected with human CTLA-4 and eGFP was stained with either (A) Goat Anti-Human CTLA-4 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems catalog # AF-386-PB) or (B) Normal Goat IgG Control (R&D Systems catalog # AB-108-C) followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (R&D Systems catalog # F0108). |
|
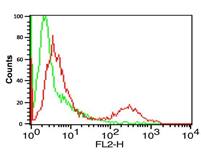 |
| Flow Cytometry: B7-H1/PD-L1/CD274 Antibody [NBP1-76769] - Analysis of A-20 cells using B7-H1/PD-L1/CD274 antibody at 0.5 ug/ml. Green: Isotype control. Red : B7-H1/PD-L1/CD274 antibody. |
|
